An adjusted trial balance is a list of all accounts in the general ledger, including adjusting entries, which have nonzero balances. This trial balance is an important step in the accounting what is product cost process because it helps identify any computational errors throughout the first five steps in the cycle. Once a book is balanced, an adjusted trial balance can be completed.
- For example, Interest Receivable is an adjusted account that has a final balance of $140 on the debit side.
- Even though they are the same numbers in the accounts, the totals on the worksheet and the totals on the balance sheet will be different because of the different presentation methods.
- All of your raw financial information flows into it, and useful financial information flows out of it.
- The adjusting entries for the first 11 months of the year 2015 have already been made.
- It is mostly helpful in situations where financial statements are manually prepared.
Frank’s Net Income and Loss
If the two balances are not equal, there is a mistake in at least one of the columns. The adjusted trial balance is the key point to ensure all debits and credits are in the general ledger accounts balance before information is transferred to financial statements. Budgeting for employee salaries, revenue expectations, sales prices, expense reductions, and long-term growth strategies are all impacted by what is provided on the financial statements. An unadjusted trial balance is a raw form of trial balance where all the general balances of the ledger accounts are directly posted and no adjusting entries are made.
4 Use the Ledger Balances to Prepare an Adjusted Trial Balance
An adjusted trial balance lists the general ledger account balances after any adjustments have been made. These adjustments typically include those for prepaid and accrued expenses, as well as non-cash expenses like depreciation. The preparation of the adjusted trial balance is the sixth step of the accounting cycle.
Best Business Bank Account for Sole Proprietor: Top Picks for 2025
If an entity is following a single-entry system, it is not possible to create a trial balance with equal debit and credit. The very first financial statement prepared is the income statement. The company will start by looking into the adjusted trial balance and taking out all the revenue and expense accounts and putting the information in the income statement. In the Printing Plus case, the credit side is the higher figure at $10,240. This means revenues exceed expenses, thus giving the company a net income. If the debit column were larger, this would mean the expenses were larger than revenues, leading to a net loss.
AccountingTools
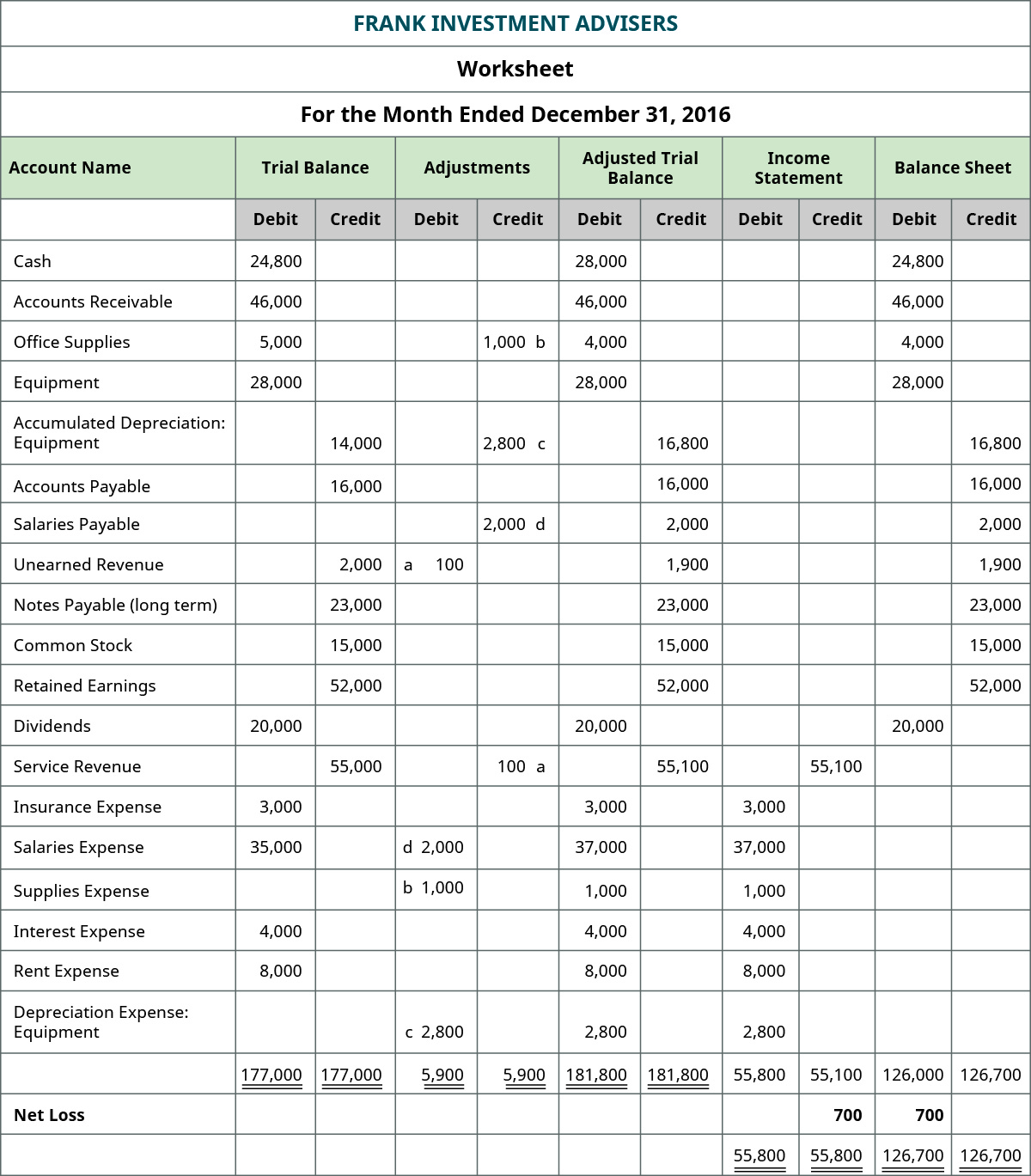
When you prepare a balance sheet, you must first have the mostupdated retained earnings balance. To get that balance, you takethe beginning retained earnings balance + net income – dividends.If you look at the worksheet for Printing Plus, you will noticethere is no retained earnings account. That is because they juststarted business this month and have no beginning retained earningsbalance. To get the numbers in these columns, you take the number in thetrial balance column and add or subtract any number found in theadjustment column. There is no adjustment in the adjustment columns, so theCash balance from the unadjusted balance column is transferred overto the adjusted trial balance columns at $24,800. InterestReceivable did not exist in the trial balance information, so thebalance in the adjustment column of $140 is transferred over to theadjusted trial balance column.
Once you’ve double checked that you’ve recorded your debit and credit entries transactions properly and confirmed the account totals are correct, it’s time to make adjusting entries. According to the rules of double-entry accounting, a company’s total debit balance must equal its total credit balance. An unadjusted trial balance is what you get when you calculate account balances for each individual account in your books over a particular period of time.
To prepare the financial statements, a company will look at theadjusted trial balance for account information. From thisinformation, the company will begin constructing each of thestatements, beginning with the income statement. The statement ofretained earnings will include beginning retained earnings, any netincome (loss) (found on the income statement), and dividends. Thebalance sheet is going to include assets, contra assets,liabilities, and stockholder equity accounts, including endingretained earnings and common stock.
Interest Receivable did not exist in the trial balance information, so the balance in the adjustment column of $140 is transferred over to the adjusted trial balance column. Remember that the balance sheet represents the accounting equation, where assets equal liabilities plus stockholders’ equity. There are multiple financial statements that are prepared by the businesses at the end of a financial year.
Run your business long enough, and you’ll accumulate a long list of debits and credits in your company’s ledger, which is a chronological list of all your business’s transactions. Note that only active accounts that will appear on the financial statements must to be listed on the trial balance. If an account has a zero balance, there is no need to list it on the trial balance. Both ways are useful depending on the site of the company and chart of accounts being used.

